Experiment Name: Study on Dobby shedding Mechanism.
Introduction:
The dobby is a shedding device placed on the top of a loom in order to produce figure patterns by using a larger number of healds than the capacity of a tappet.
Objectives:
- Know about the dobby shedding machine.
- Know about the machine parts involved in this mechanism.
- Learn the working procedure of this mechanism.
Types of Dobby Shedding in Textile Weaving:
Dobby shedding is classified into below types:
-
According to the figuring capacity:
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, ……………, 36
-
According to the position of dobby with loom:
- Vertical loom,
- Horizontal loom.
-
According to lift:
- Single acting or single lift,
- Double acting or double lift.
-
According to the driving of heald shaft:
- Positive,
- Negative
-
According to the type of shed:
- Open shed,
- Bottom close shed,
- Semi-open shed.
-
According to no jack lever:
- Single jack
- Double jack
-
Source of control:
- Mechanical dobby,
- Electric dobby.
-
Broadly:
- Ordinary dobby,
- Special dobby.
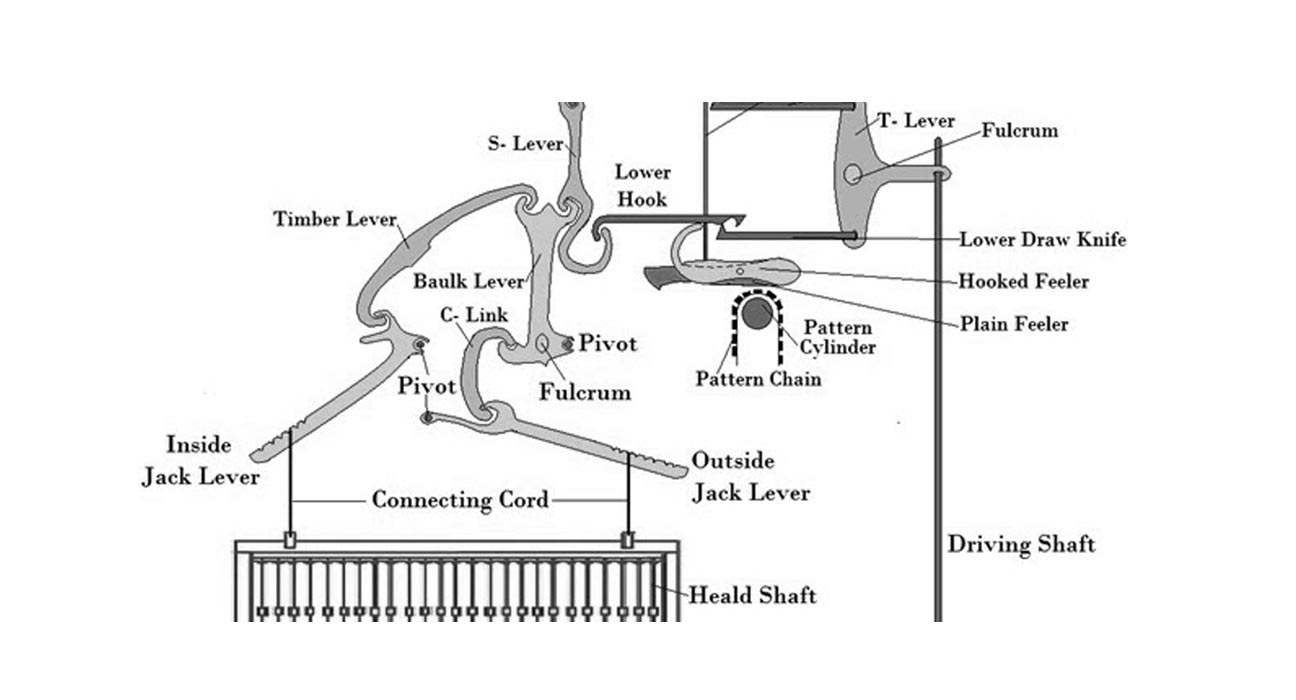
Main parts:
- Bottom shaft
- L-lever
- Upright shaft
- T-lever
- Upper delineate knife
- Lower delineate knife
- Upper hook
- Lower hook
- S-lever
- Bulk lever
- Thumb lever
- Jack lever
- Heald-shafts
- Returning spring
- Motor
- Crank shaft
- Pattern cylinder
- Pattern chain
Mechanism:
Positive Dobby Shedding Mechanism:
Principles of positive dobby, in this variety of shed lifting & lowering of the heald frame, each is possible. lifting is occurred by means of a jack & lever, and lowering is occurred by means of spring under tension.
Positive dobby shedding is the combination of 3 Cylinders, jack lever, spring and a shaft. Between the 3 cylinders, a shaft is a pin in one side the upper cylinder moves because the opposing clockwise and lower cylinder moves because of the clockwise direction. the main cylinder when getting motion from the shaft when it found peg or pattern plan then the cylinder connected to the higher half-toothed disc. so the heald frame is up, & when the pattern cylinder doesn’t found peg then the main cylinder connected to the lower half-toothed disc and also the spring retains the heald frame to the downward direction
Figure: Positive Dobby.
Negative Dobby Shedding Mechanism:
When the connecting rod moves up and down and T-lever gives outward and inward movement. According to fabric design, when peg comes in contact with the feeder, then the right portion of feeler is raised and the left portion being lowered. Hooks are lowered as hooks are supported with feeler. When the left end of feeler is lowered then the upper hook came in contact with the upper knife. In this state, when connecting rod moves down, the upper portion of T-leavers gives outward movement. As a result, upper portion of S-lever, baulk lever also moves to the right side. Thus, a pull creates on timber lever and link.
As outside and inside jack lever joined with the timber lever and link, the lever moves up at the same time. Hence, the heald shaft rose up.
Similarly, when the left end of the feeler is lowered then the lower hook comes in contact with the lower knife. In this case, when connecting rod moves up and the bottom portion of T-lever moves to the right side. As a result, bottom portion of S-lever moves to the right and the same process occurs i.e. top portion of the baulk lever moves to the right. Here, jack levers are moved at the same time.
Hence, the heald shaft again rose. Thus, a heald shaft is alternatively rose by the lower knife and upper knife. The shaft will therefore be lowered with the help of return spring and will remain down for the next pick.
Read: Study on Tappet shedding Mechanism
Figure: Negative Dobby.
Major uses of dobby shedding:
In the cotton industry, maximum 24 shafts dobbies are used. But mostly 16 to 20 shafts are used.
In worsted industry, dobbies with 36 jacks are in uses and many of them are positive in action and suitable for heavy shedding.
The chance of pattern in the fabric, in dobby loom, can be readily done where as it is laborious and expensive in case of tappet.
Dobbies offer better facilities for producing a variety of patterns with a greater number of healds than that is possible with tappets.
Dobbies are extensively used for weaving twill, sateen and other simple weaves.
Conclusion:
This practical will help to make understand the dobby shedding mechanism, parts involved in mechanism and working process of dobby shedding mechanism of a dobby loom.