Revolutionary Ideas of Textiles. Some revolutionary ideas of Textiles include E-Textiles, Smart Textiles, Nano fabrics. Evolution of Textile.
E-Textiles
Often, you hear about e-commerce, e-banking, e-mail, e-learning, but have you ever heard about the term “E-Textile”? If you not, then let’s know about e-textile.
The term e-textile stands for “Electronic Textiles”. Electronic textiles are fabrics that enable digital components such as a battery and light and electronics to be inserted in them. Electronic textiles are a recognizable form and wearable computing because the emphasis is placed on the consistent unification of textiles with electronic elements like microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. Furthermore, e-textiles need not be wearable. For instance, e-textiles are also found in interior design.
A new report from Cientifica Research examines the markets for textile-based wearable technologies, the companies producing them, and the enabling technologies. The report identifies three distinct generations of textile wearable technologies:
These are:
- First-generation: Attach a sensor to apparel. This approach is currently taken by sportswear brands such as Adidas, Nike, and Under Amour
- Second-generation: Products embed the sensor in the garment, as demonstrated by current products from Samsung, Alphabet, Ralph Lauren, and Flex.
- Third-generation: Wearable, the garment is the sensor. A growing number of companies are creating pressure, strain, and temperature sensors for this purpose.
Future applications for e-textiles may be developed for sports and well-being products, and medical devices for patient monitoring. Technical textiles, fashion, and entertainment will also be significant applications.
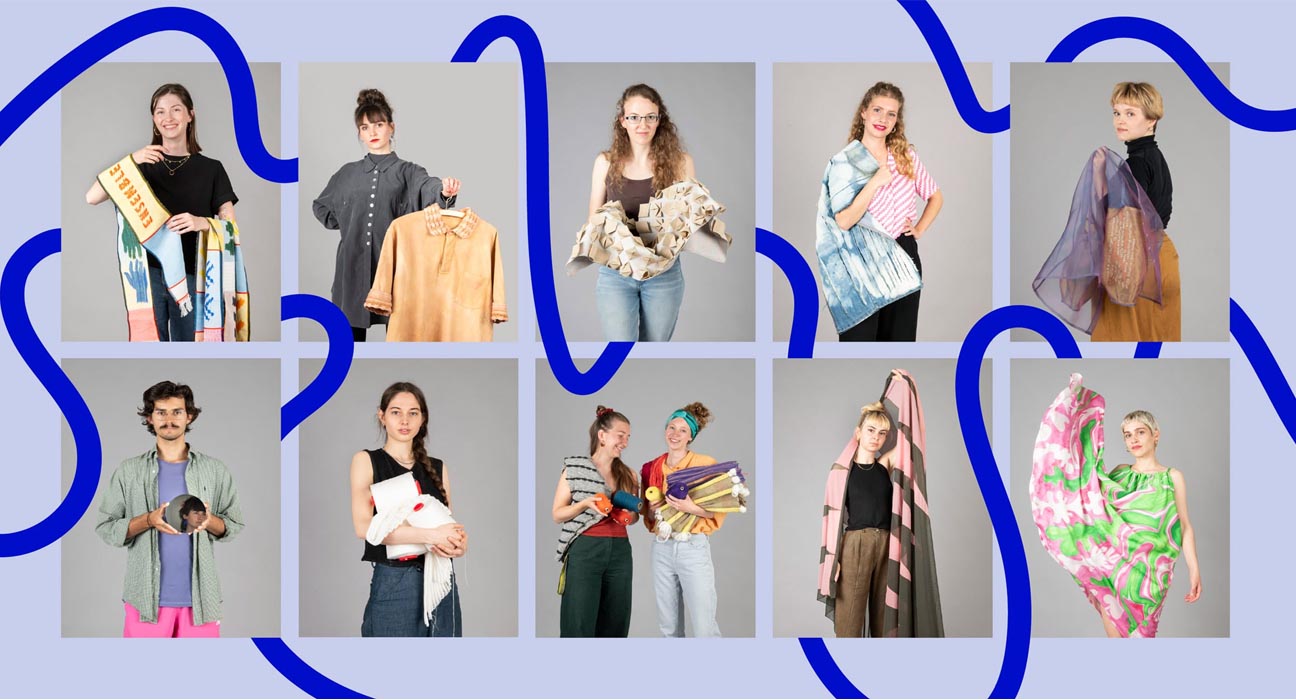
Some examples of E-Textiles
The term ‘smart textiles’ is derived from intelligent or smart materials. The concept ‘smart material’ was defined for the first time in Japan in 1989. The first textile material that was labeled as a ‘smart textile’ was silk thread having a shape memory. The inventory of shape-memory materials in the 1960s and intelligent polymeric gels in the 1970s were generally accepted as the birth of real smart materials.
Pailes-Friedman of the Pratt Institute states that “what makes smart fabrics revolutionary is that they have the ability to do many things that traditional fabrics cannot, including communicate, transform, conduct energy, and even grow”.
Smart textiles are described into mainly two categories:
- Aesthetic.
- Performance enhancing.
Aesthetic smart textiles:
The fabrics that light up and fabrics that can change color are included into aesthetic smart textiles. Some of these fabrics gather energy from the environment by harnessing vibrations, sound, or heat, reacting to these inputs. Electronics that can power the fabric can be also inserted to change the color and lighting scheme of smart textile.
Performance enhancing:
The fabrics that are used in those fields in which the enhancing of performance is needed with the collaboration of body, surrounding environment are identified as performance-enhancing smart textiles. They can be used in athletic, extreme sports, and military applications which are performance-enhancing fields. These textiles are customized for use in these include fabrics designed to regulate body temperature, reduce wind resistance, and control muscle vibration. All of which may improve the above-mentioned field’s performance.
Other fabrics have been developed for other purposes like protective clothing, guard against extreme environmental hazards (such as radiation and the effects of space travel). The health and beauty industry is also taking advantage of these innovations, which range from drug-releasing medical textiles to fabric with moisturizer, perfume, and anti-aging properties.
Revolutionary Ideas of Textiles
Some examples of smart-textiles
Nano fabrics
Nano fabrics are textiles engineered with small particles. Especially these types of fabrics are given extra-ordinary characteristics with ordinary materials advantageous properties.
These properties are:
- Superhydrophobicity . (extreme water resistance)
- Odor and moisture elimination.
- Increased elasticity and strength.
- Bacterial resistance.
A nano fabric is either produced from fibers called nanofibers, or is created by applying a solution containing nanoparticles to a regular fabric.
Properties of Nano Fabrics:
As it is a productive unique concept of fabric,it has a definite width of less than 1000 nanometers which is often called nanofiber . In this nanofiber there are nanoparticles which can be described as a small group of atoms or molecules with a radius of less than 100 naometers . These particles have a very high surface area to volume ratio on the nanoscale. This high surface area to volume ratio is seen in very small particles what makes it possible to innovate many specific properties existed by nanofabrics.
Nano Fabrics Manufacture Process:
Nanofabrics are predominantly manufactured with the process of “sol gel and “electro spinning”.
- Sol gel: It is a gel like solution which is applied to textiles to create the novel properties of nanofabrics as a liquid finishing ingredient .This process begins by dissolving nanoparticles in a liquid solvent. As the solvent, mainly alcohol is used .After dissolving some chemical reactions happen to grow and form a linkage throughout the liquid .This linkage converts the solution into a colloid. In the next steps, the solid particles must undergo a drying process to remove excess solvent from the mixture so that it can be used as a fabric.
- Electro spinning: The process in which the nanofibers are extracted from polymer solutions and assembled them to create nanowoven nanofabrics, is known as electro spinning. In the first step, to charge the polymer strands, a strong electric field is applied to the solution. After that, the solution is placed into a syringe and targeted at an oppositely charged collector plate. When the force of attraction between the polymer nanofibers and the collector plate exceed the surface tension of the solution, the nanofibers are released from the solution and gather onto the collector plate.
Revolutionary Ideas of Textiles
Applications of Nano Fabrics:
The application fields of nanofabrics are huge. It is chiefly used in:
Textile Manufacturing:
Nowadays, to produce modern textiles and RMG nanofibers are used largely. It has advantages like odor and moisture elimination , highly water resistancy , bacterial resaistancy and last but not the least , it can increase the physical strength like elasticity of a RMG .This is why. It is used to produce highly qualified hand gloves, shocks and moreover to produce our daily needed garments also.
Drug delivery:
The nanofabrics is used in medicine delivery like antibiotics, anticancer drugs ,proteins and DNA precise quantities.It is also applied to the tissue of target area that carries the desire drug with it. The rate of the drug administered can be also changed by altering the composition of the nanofabnrics.
Tissue Engineering:
The nanofabrics which are made by electro spinning, have the potential to help in the growth of organ tissue, none, ligaments, tendons, neurons etc. It also can be used to support the damage tissue.
About the Author
MD. SHANAWAZ KHAN
Pabna Textile Engineering College
Department of Apparel Engineering
Join Our Fb Group